Contract Research Organisation (CRO)
A Contract Research Organisation (CRO), or Clinical Research Organisation, has a pivotal role in drug development. The CRO you’ll start working with directly impacts your success in all phases of clinical trials. TRACER is an imaging CRO. We label your compound with a radioactive or fluorescent dye. In-human imaging during clinical trials offers valuable data. Furthermore, we specialize in early phase clinical trials (Phase 0, 1 and 2). With TRACER you can move your compound fast in-patient, already ahead of Phase I. Learn more about our contract research organization services.
Request the information package on clinical trials regarding your compound.
TRACER contract research services
TRACER is a full-service contract research organization for early phase clinical trials. Our regulatory, operations, and clinical teams support biotech and pharma from preclinical studies to finalizing Phase 2.
We have extensive experience in optical and nuclear imaging techniques, providing valuable insights for drug developers during the early phase clinical trials.
Translational
Clinical translation
As a contract research organisation, you can involve us from the moment you want to start your preclinical work. TRACER CRO can reduce the preclinical phase as allowed by ICH M3 R2 guidance. Our Imaging solutions for clinical trials allow researchers to make better decisions in both the preclinical and clinical phases of drug development.
Improving lead candidate selection and obtaining preliminary in-human data can increase the overall chance of success for new therapies. We take care of the preclinical part and clinical translation of your compound. Included in our preclinical/translational services are quality control, method development, validation, purification, labeling, and toxicity and biodistribution studies.
Request services list
GLP vs GMP
As our contract research laboratory will label your investigational new drug for imaging under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) conditions, Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) is often sufficient for your exploratory trial. Saving costs on GMP at this stage is another benefit of adding imaging to clinical trials. Of course, for Phase I you will need GMP material of the unlabeled study drug. However, based on the exploratory trial results, you may need to alter your lead compound before further development.
Regulatory changes provide drug developers with more possibilities
Under ICH M3 guidance, drug developers can perform lead compound selection in humans rather than in animal models. Potentially eliminating issues from inter-species variations. Furthermore, microdose data extrapolation can be considered more reliable than allometric scaling. Allometric scaling vs microdose extrapolation results in 68%-94% vs 45% accuracy respectively [1]. There are more recent regulatory changes for faster and more cost-effective development than most drug developers know. Contact TRACER CRO to discuss what applies to you.
Casette microdosing
TRACER contract research organisation aims to go as fast into patients as possible while adhering to all safety standards. With a cassette microdosing trial, it is possible to test up to 5 different variations of your compound in-human. Allowing to decide on what lead compound to develop under GMP conditions based on in-human data instead of data from animal models.
Eliminating inter-species variations
Not reaching the clinical endpoints may terminate the development of your compound. But how do you know if this is not the result of a false negative? Preclinical inter-species variations can affect study results. Thus, moving into the patient population as fast as possible gives a more realistic perspective. Imaging can be used in Phase 0 first in patient clinical trials to obtain necessary data. Allowing drug developers to evaluate in-human behavior before the traditional Phase 1 first in human study. The purpose of the first in human study is to reproduce and validate preclinical results. A Phase 0 imaging trial does exactly that.
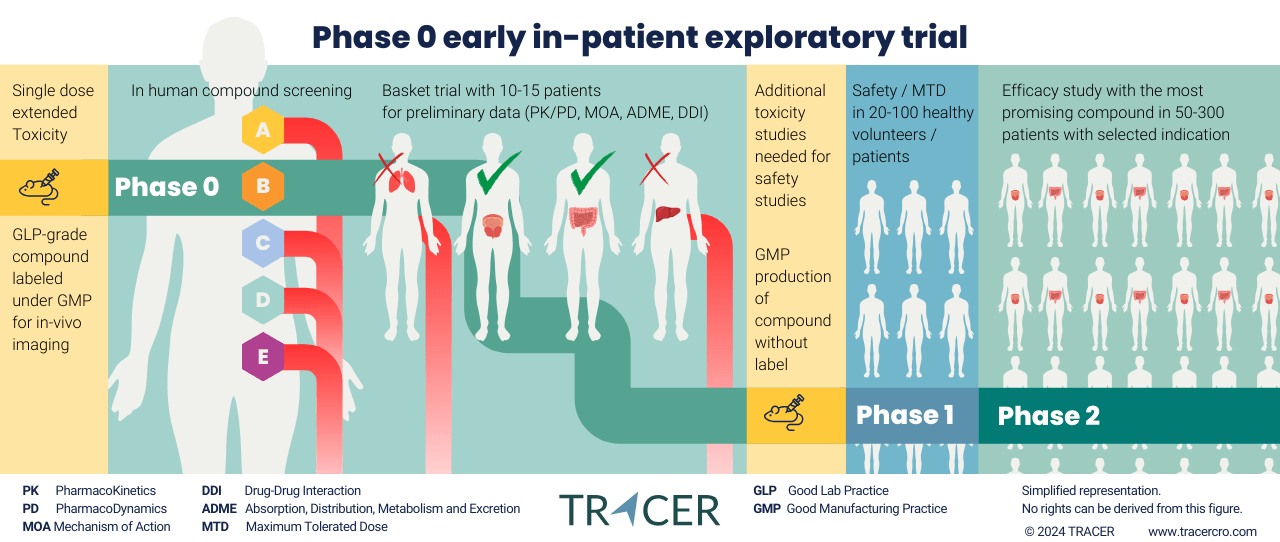
Phase 0 CRO
Phase 0 contract research organisation
TRACER is well-known as a Phase 0 contract research organisation. Over the past years, we’ve advised hundreds of life science companies on Phase 0. We always start by making a comparison between Phase 0 or Phase 1 studies. Your best starting point depends on your compound and indication.
For instance, Phase 0 is commonly an in-patient study. Phase 1 is often conducted on healthy volunteers, but can be conducted in-patient for certain compounds and indications. What is for you the best first in-human study? Fill out the questions below to find out.
Phase 0 or Phase 1 for your first in-human study?
Read more about the Phase 0 clinical trial.
Phase 1 CRO
We can check if your compound is suitable for Phase 1 in-patient studies. Contact us to discuss.
Phase I Clinical Research Units
TRACER has access to state-of-the-art Clinical Research Units (CRUs). The units are used for clinical trial conduct. Operated by specialized personnel, experienced in trial conduct. This controlled environment, allowing for intensive monitoring by medical supervisors, provides maximum safety for participants. TRACER Phase 1 units are especially useful for clinical trials with healthy volunteers. We conduct our clinical trials with patients in the hospital. In both cases TRACER ensures work is done according to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) and the sponsor’s instructions.
Phase 1B / 2A CRO

If you are already in Phase I, imaging can be used in a Phase 1B or 2A study to obtain proof of concept. The Proof of Concept studies (PoC study) we provide as contract research organisation are relatively fast. Results can be used for study design and to raise funding for more expensive trials with large populations.
Phase 2 CRO
Phase 2 contract research organisation
Traditionally, and depending on the compound, contract research organizations offer Phase 2 as the first in-patient clinical trial. Phase II studies measure the biological effect of the compound in terms of efficacy and side effects on patients. Historically the failure rate in the Phase II clinical trial has been the highest, making it the most critical in drug development. Increasing the chance of success in Phase II regarding efficacy already starts in the exploratory phase.
Exploratory trials to prepare for Phase 2
Because at TRACER we already obtained Pharmacokinetics (PK) and BioDistribution (BD) data in Phase 0, Phase 2 is no longer the first time to study your compound in-patient. We already know what indications to include and exclude in your Phase 2 trial. We’ve obtained the needed data from a smart clinical trial design in Phase 0, such as a basket trial or adaptive trial.
Lowering the high failure rate of investigational new drugs
The rate of new drugs that make it through all phases of clinical trials has been around 10% for years [2]. This number is based on drugs failing in the clinical phase. The success rate would be even lower when considering also drug development programs failing in drug discovery or preclinical. Preclinical contract research organisations could play a role in lowering the failure rate by improving compound screening. Clinical research organisations can contribute to a higher success rate with smart clinical trial designs. TRACER combines the work of clinical and preclinical contract research organisations. Offering drug developers an approach beyond the conventional drug development process.
About TRACER
TRACER originated in the clinic. Translating the concept of image-guided surgery to in-human imaging of a compound in drug development. Similar to imaging tumor tissue with fluorescence, a new drug can be imaged to show binding to its target. Imaging in clinical trials is possible in many areas and is not limited to oncology. Furthermore, many imaging techniques are available, such as fluorescence, nuclear imaging (PET/SPECT), and RAMAN imaging. We urge biotech and pharma to use the full extent of imaging in clinical trials to comprehend the behaviour of their compound.
Learn more about imaging for clinical trials. Book a knowledge session with TRACER.
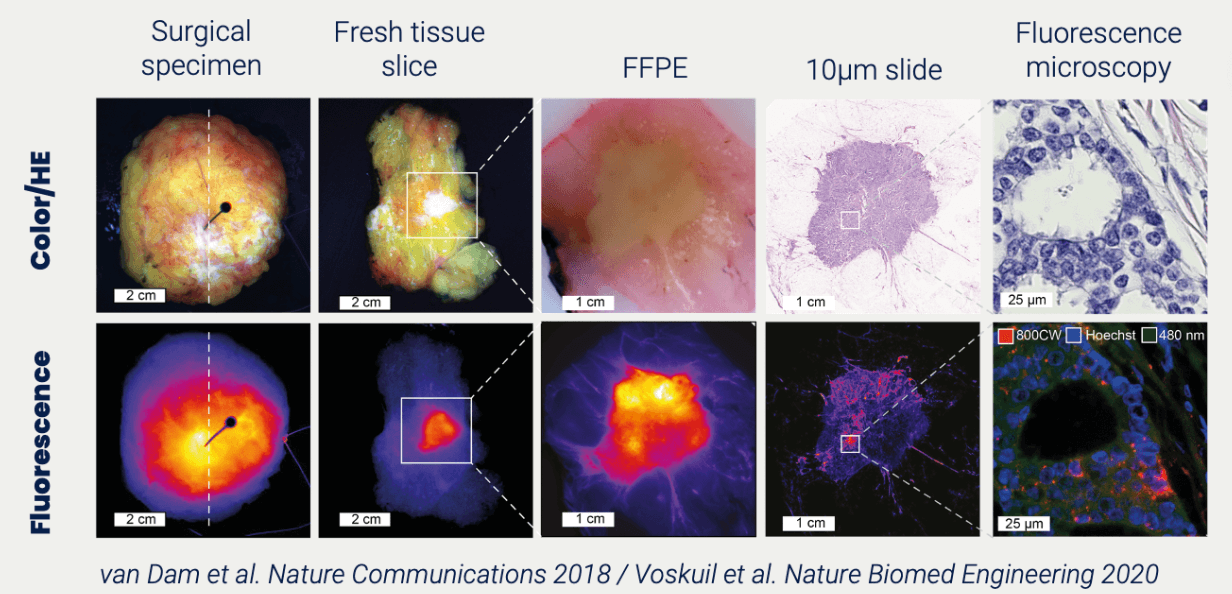
Exploratory trials and enhancing decision-making
As a contract research organisation, we specialize in exploratory trials and adding imaging techniques to many different types of clinical trials to enhance decision-making.
“Don’t focus on what you think you know in the clinical trials design, instead leave room to discover what you don’t know. Move into patients as fast as possible, data from healthy volunteers or animal models is often not representative of your patient population.”
— Maarten Brom, PhD (VP Technology Assessment)
Exploratory trial approaches
Explore possibilities in early phase clinical trials with the FDA Critical Path Initiative and EMA equivalent programs. TRACER contract research organisation empowers biotechs with these new opportunities to accelerate drug development. For instance, have you considered:
- In-patient screening of multiple compounds as addition to the preclinical stage;
- Exploratory basket trial to study target indication/population and disease variation;
- First in-patient microdosing study for preliminary data (PK/PD, MOA, ADME, DDI);
- In-patient dose escalation from sub-therapeutic into anticipated therapeutic range (non-microdosing study).
All the options still fall under exploratory trial regulations and can be conducted before Phase 1.
Informed clinical trial decision-making with imaging.
Imaging in clinical trials can enhance early decision-making.
- Imaging in early in-patient Phase 0 microdosing studies provides information on efficacy in different patient populations.
- Imaging provides early detection of treatment response, that might not be visible in biomarkers or other clinical endpoints.
- Imaging helps determine the areas of interest, both where treatment can have an effect, and where side effects are likely to occur.
- When investigating toxicity, imaging can visualize drug accumulation throughout the body.
- Imaging and basket trials go hand-in-hand, allowing to stratify patient populations based on disease characteristics and treatment response.
- Imaging provides target validation.
Full-service contract research organisation for pharmaceuticals and devices
We are a full service clinical research organization, conducting studies for pharmaceuticals and medical devices. We take everything off your hands, starting with a labeling strategy and study design, up to medical writing, regulatory compliance, and study conduct. We specialize in the early Phase clinical trials. Including exploratory studies (Phase 0), Phase I (1a & 1b), and Phase 2 (2a & 2b).
Pharmaceutical contract research organization
You can hire TRACER as your pharmaceutical contract research organization. We are experienced in pharmaceutical clinical trials. Whether a compound is an antibody, peptide, small molecule, radiopharmaceutical, or of any other type; we are confident we can label your compound for imaging during the clinical trial. At the intake, which you can book below, our VP Molecular Imaging will discuss labeling of your compound for imaging.
Book your intake with TRACER.
Medical device contract research organization
TRACER can design, submit, and conduct your medical device clinical trials. This includes first in-human medical device trials. For example, medical device imaging can show how the device behaves in-human. In one of the medical device trials, we used imaging to track the trajectory of the device and verified the mechanism of action in-patient.
FAQ
Based on many conversations we had with life sciences and biotech companies we’ve written down the most common questions and our answers. TRACER specializes in first in-human studies. In early Phase clinical research, the first in human study is the most pivotal. The first in human phase bridges the gap between preclinical and clinical. By replacing a part of the preclinical drug development with exploratory in-human trials, such as Phase 0, we move compounds faster into the clinic. Allowing drug developers to save precious time, obtain early proof of concept, and make an accurate and fast go/no-go decision for a lead compound candidate. TRACER is a contract research organization with headquarters in the Netherlands. Via our clinical research network, we offer global contract research organization services. However, since we are based in Europe, we maximize the advantages of local and EMA fast regulatory approval processes. Contact us for an optimal clinical site location. There are several reasons to consider partnering with a clinical research organisation in Europe. Conducting clinical trials in Europe is often fast due to fast regulatory approval. But the advantages don’t end there. Two disadvantages of EU clinical trials to take into consideration are relatively higher costs compared to more emerging markets and potential linguistic challenges. Outsourcing clinical trials is a standard practice in drug development. Many drug developers work with a contract research organisation for clinical outsourcing. Outsourcing is providing drug developers with instant access to the expertise and existing infrastructure of a CRO. A full service CRO already has all protocols in place, from regulatory submission to data management. Different specialists are involved in clinical research. By outsourcing clinical trials to a CRO, you don’t need in-house personnel. TRACER is a pharmaceutical contract research organisation. We work in the biotech sphere, so our clients are mostly pharmaceutical companies, independent drug developers, academia, and university spin-offs. Our clients range from large pharmaceutical companies to small biotech start-ups. As needed in the early phase of drug development, we provide services within the scope of a contract research laboratory and pharmaceutical contract research in the clinic. Why would you choose to work with a smaller contract research organisation instead of the top contract research organizations? Often small CRO companies are highly specialized. For TRACER, the specializations are imaging and exploratory trials. For you as a drug developer, the notable advantage is the dedication to your project that a small CRO can offer. This trickles down to the clinic because there is continuous personal contact between the CRO and the clinic. In general, there is a high level of flexibility. A small contract research organisation can tailor the situation to the needs of you as a client. Whereas with larger CROs deviating from protocols can be challenging or impossible. Moreover, costs may be lower due to lower overheads. The expertise of a pharmaceutical clinical research organization mainly consists of compound/device type, therapeutic area, technique, subjects (patients or healthy volunteers), and phases of drug development (early phase / late-phase drug development. E.g., a dermatology contract research organization specializes in skin, nail, and hair conditions while oncology contract research organizations focus on cancer therapies. The choice in CRO can depend on your compound, but also on phase of development and technology. To elaborate further, at TRACER we often use imaging methods such as fluorescent and Raman in dermatology. In oncology clinical trials, targeting deeper tissues, we use PET/SPECT. Yes, it is not uncommon that drug developers choose for early phase clinical trials small contract research organizations due to a specialty. For the large Phase 3 clinical trial, a larger CRO can be chosen. An important aspect to understand from contract research is that if a study is conducted properly and well-documented, other researchers can easily continue or cooperate. The best contract research organization is the one meeting your needs the best. Where the contract research organization services are within the scope of your research and where the expertise of the CRO delivers you more relevant data from the same clinical trial. Contract research organization companies support pharmaceutical and medical device companies in their research. Contract research can be found in every phase of drug development, from discovery to clinical trials and pharmacovigilance. Contract research organisation is an umbrella term. What a contract research organisation does, depends on its type and niche. We compare below this FAQ the most common types of CROs and discuss the scope of their work.
Why do you need an early phase CRO?
Is TRACER a global contract research organization?
Why choose for your clinical research organization Europe?
Why choose for contract research outsourcing?
Who are our clients?
What are the advantages of small contract research organisations?
What are the different kinds of expertise for clinical research organisations?
Can I switch between clinical research organization companies?
What is the best contract research organization?
What does a contract research organization do?
Differences between research companies explained
There are several types of research organisations with similarities and differences. The goal is to find the best matching CRO in research for your program.
Types of CROs
There are multiple types of CROs.
- A clinical research organisation is a contract research organisation solely concerned with clinical studies.
- Drug discovery contract research organizations, do not conduct studies in human, but support drug developers in the discovery process.
- A preclinical CRO conducts laboratory and animal studies.
- A bioanalytical CRO specializes in method development and validation.
- A clinical trial organisation is concerned with the management of clinical trials.
As stated before, clinical research organization companies can be specialized in pharma or devices, certain compounds or devices, and areas of interest. In addition to these types of CROs, there are related organizations and specialists, such as regulatory affairs consultants, data management providers etc.
Clinical contract research organisation vs preclinical contract research organization
A preclinical contract research organization focuses on laboratory research such as animal studies and in-vitro studies. A clinical contract research organization conducts studies on human subjects. Clinical research involves more regulation, patient recruitment, and monitoring. For you, as a drug developer, it is important to know that part of the late preclinical phase can be replaced with exploratory clinical trials under ICH M3 guidance. TRACER can work together with your preclinical CRO to ensure a smooth translation into the clinic.
Contract research organization vs medical research organization
What is the difference between a contract research organization and a Medical Research Organization (MRO)? While both definitions are comparable, there are some differences. A contract research organization is a service provider, while a medical research organization often conducts research on its own initiative. For instance, an MRO can be an academic, government, non-profit, or private institution. Their research scope does not have to be focused on drug development and can also include disease mechanisms, health trends, and risk factors. In other words, an MRO can work as a stand-alone organisation, where contract research organization pharmaceutical companies always work together.
Clinical research organisation vs contract research organization
What is the difference between a clinical research organization and a contract research organization? The definitions clinical research organisation and contract research organization are highly interchangeable. A clinical research organisation is a type of CRO, that primarily performs research in the clinic, meaning patient studies. There are multiple types of clinical research organizations. The biggest difference is in CRO pharma vs CRO for medical devices. A drug development CRO, meaning pharma, can be specialized in types of compounds. For medical device CROs, differentiation is in the type of device, e.g., surgical equipment, wearables, diagnostic/imaging systems, drug delivery devices, etc.
Site Management Organization vs CRO
The SMO Site Management Organization provides support at the research site. This is often in the hospital. Site management can also be a separate function at a clinical contract research organisation or can be part of the project manager’s tasks. At TRACER our physician-scientists are performing the tasks of the SMO organization. Meaning we provide this as an in-house service; our physician scientist works at least one day a week at the site. Tasks of site management organisation in clinical research are study start-up, study conduct, patient recruitment, and quality assurance. By working at the hospital, and being present at relevant handover meetings, good relations and short lines of communication are assured.
CDMO vs CRO
CDMO stands for Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization, but can also be referred to as contract research and manufacturing organization. In the past, it was referred to as CMO (Contract Manufacturing Organization), but to avoid confusion with abbreviations for Chief Medical Officer and Clinical Monitoring Organization, the D from Development was added. A CDMO differs from a CRO in the manufacturing/development aspect. Often a CDMO manufactures the material for the clinical trials but can assist drug developers at a wider scale, from formulation development to eventually commercial production. They can manufacture for the contract research organization clinical trials materials.
TRACER as your device and pharma contract research organization
This article gave you the general outlines of the scope of the contract research organization industry. It showed how a clinical trial organization fits in the complete picture of contract research pharma. The only question remaining is how TRACER matches your requirements as an early phase contract research organization. To answer this question, we are happy to schedule 30 minutes of our time for you. During this call with our experts, you can ask anything about labeling your compound for imaging and study design. Please fill out the meeting request form, so we can include the right experts on the call for you. After the call, you can receive a budget and timeline for your project.
Take me to the meeting request form
Abbreviations
|
CRO |
Contract Research Organisation / Clinical Research Organisation |
|
ICH |
International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use |
|
GMP |
Good Manufacturing Practices |
|
GLP |
Good Laboratory Practice |
|
siRNA |
Small interfering RNA |
|
RNAi |
Ribonucleic acid interference |
|
CRU |
Clinical Research Unit |
|
PoC |
Proof of Concept |
|
GCP |
Good Clinical Practice |
|
PK |
Pharmacokinetics |
|
BD |
Biodistribution |
|
PET |
Positron Emission Tomography |
|
SPECT |
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography |
|
FDA |
Food and Drug Administration |
|
MOA |
Mechanism Of Action |
|
ADME |
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion |
|
DDI |
Drug-Drug-Interaction |
|
EMA |
European Medicines Agency |
|
MRO |
Medical Research Organisation |
|
SMO |
Site Management Organization |
|
CDMO |
Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization |
|
CMO |
Contract Manufacturing Organization / Chief Medical Officer / Clinical Monitoring Organization |
Citations
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41573-020-0080-x
2. Chi Heem Wong, Kien Wei Siah, Andrew W Lo, Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters, Biostatistics, Volume 20, Issue 2, April 2019, Pages 273–286, https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxx069
https://academic.oup.com/biostatistics/article/20/2/273/4817524